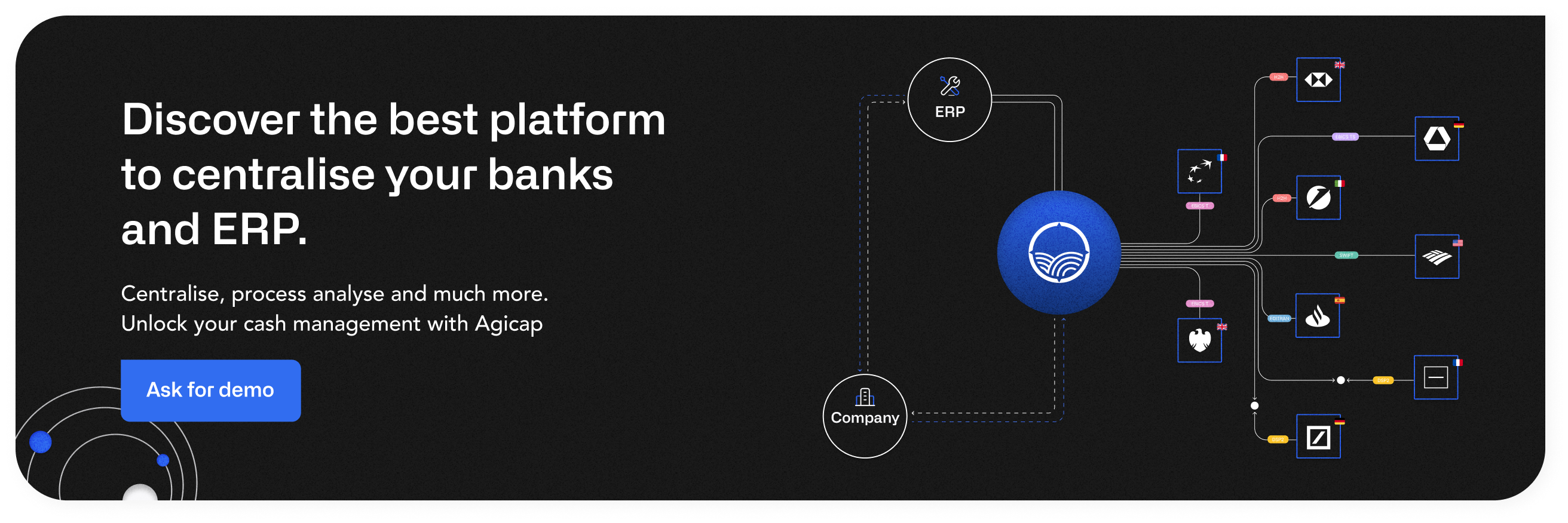
Banking Networks, Protocols and Formats You Should Know About


Establishing banking connectivity is as a typical instance of a make-or-buy decision for businesses that may already possess in-house solutions for the majority of their operations. However, creating and maintaining bank connections can be quite demanding. It involves a significant amount of work, not only in terms of initial paperwork but also regarding ongoing maintenance. A good example is,, when using H2H (Host-to-Host), your bank is free to alter connection protocols, file formats, or even security guidelines whenever it wants, which can complicate the sustainability of your connectivity.
Why Companies Look for a Banking Connectivity Solution
To alleviate this burden, companies frequently collaborate with banking connectivity-as-a-service providers who supply the necessary banking connections, assist in their successful establishment, and manage their maintenance. This approach is especially time-efficient and effective when dealing with numerous banks to connect with, as well as when incorporating new banks into your system through mergers and acquisitions. The primary advantage of banking connectivity-as-a-service lies in the autonomy it grants companies from banks, eliminating the need to depend on a specific bank's online banking tool and to manually upload and download data each time.

Even when opting for a banking connectivity-as-a-service provider over developing it in-house, there are several banking protocols and networks to be aware of before determining which one to utilise for your connectivity. Simultaneously, the channel represents only a portion of the equation. There are various file formats, security measures, and encryption practices to take into account when making your decision. In the following, we will present you some of the most well-known banking networks, protocols and formats, without attempting to be exhaustive on the topic.
Direct Host to Host Connections with H2H
H2H connections are a fundamental method for obtaining bank account data, requiring adherence to bank guidelines and a dependable IT department for implementation and maintenance. These connections can be established using SFTP servers or other techniques like SOAP, FTPS, and AS2, providing secure, encrypted communication between banks and companies. H2H offers benefits such as direct and secure connections, reduced risk, and accurate banking information, especially when using a banking connectivity-as-a-service interface for balance reporting, payments, and cash flow planning.
However, H2H connections also have drawbacks, including lengthy integration periods, potentially high implementation and maintenance costs, and expensive payment processing. Implementing a single bank's server can take 2-3 months, with additional time needed for complete setup if multiple bank accounts are involved. One-time implementation and monthly fees can range from a few hundred to several thousand Euros, and processing payments can be costly, making it essential to negotiate lower prices since banks do not provide public price lists for these services.
The European Standard of EBICS
EBICS, a banking protocol introduced in 2006, is an internet-based communication and security standard widely used in Europe. It enables secure and effective combat against payment fraud and ensures accurate, up-to-date data in ERP software or treasury management systems. EBICS T and EBICS TS, additional versions, improve data communication security by requiring an extra signature for transaction authorization. This protocol has reduced paperwork, increased security, and is close to becoming the pan-European standard for bank communication in many countries.
The main advantages of EBICS include its affordability, ease of implementation, adaptability to multiple banks, and decentralised, secure communication. However, one disadvantage is the existence of different local versions with varying encryption and technical specifications. EBICS 3.0 aims to resolve this issue by aligning all local banks to a single international data transfer standard.

The Huge Network of SWIFT
SWIFT, a global banking network, provides immediate access to over 10,000 banks in more than 200 countries, offering a single, secure, and reliable gateway for changing banking partners without establishing new connections. However, joining SWIFT is time-consuming due to a lengthy application and screening process, and costs rise with the amount of data processed. SWIFT is widely used for centralising cash positions, aggregating bank statements, and transmitting local and international payments through SWIFTNet.
The capacity to consolidate global cash positions through a unified conduit constitutes a significant advantage of the SWIFT network. This system facilitates the amalgamation of bank statements and comprehensive cash aggregation, which is a primary application of SWIFT. While transactions are frequently executed at a local level utilising regional connectivity methods such as EBICS and Editran, information reporting transpires at the group level. Consequently, SWIFT is extensively employed to centralise bank statements.
The main advantages of using SWIFT include well-maintained, fast, and reliable financial data transfer, and its global reach, making it ideal for international business. The main disadvantages are the potential for delayed payments due to intermediary banks, especially in international transfers, expensive fees, and high exchange rates that can cause cash flow problems.
Open Banking with PSD2
PSD2 connections, resulting from the Second Payment Services Directive, promote open banking by mandating banks to provide access to clients' accounts through APIs. This allows clients to take control of their financial data and manage finances through third-party services, with security upheld by two-factor authentication. However, APIs currently lack the same information capacity and reporting abilities as other protocols and networks, and their technical implementation can be complex due to compatibility requirements with different banks.
The main advantages of using PSD2 include enhanced security requirements, the emergence of need-specific financial services, and real-time access to banking-related data. The main disadvantages are its lower reliability compared to traditional banking protocols, inferior data quality, and the complexity of implementing PSD2 APIs. Additionally, PSD2 is limited to banks operating within the European Economic Area (EEA), making it difficult to build connectivity with global banks.
Format of Choice: ISO 20022
When dealing with banking connectivity, there are various advantages and disadvantages to specific protocols and networks. However, the ISO 20022 standard, introduced in 2004, provides a safe choice for multinational corporations. This XML-based format surpasses traditional MT-formats in use and popularity, and is recognized as the future of the banking industry due to its high level of standardisation, allowing for increased automation, efficiency, and risk reduction.
Despite the benefits of ISO 20022, not all banks are up-to-speed in offering banking connectivity options and handling all formats for sending and receiving banking data. Therefore, it is crucial to check with your bank to determine what is possible and what kind of solution is needed for communication with a particular bank.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the various banking protocols and networks discussed provide comparable levels of security and adaptability. However, they necessitate differing degrees of time and financial investment for successful implementation. To optimise cost-efficiency and gain greater control over the implementation timeline, it is advisable to explore a banking connectivity as-a-service solution. By engaging a single provider to manage the entire setup process, you can streamline expenses and enhance overall efficiency.
Over 7.000 companies already use Agicap as a banking connectivity as-a-service, including many more features for cash flow management and related financial processes. Ask for a demo here.

